In this article, Forex Prop Reviews will explain interest rate swaps, how they work, and their benefits.
Interest Rate Swaps: How They Work and Their Benefits
Interest rate swaps are financial agreements that allow parties to exchange interest payments on a specified principal amount. They are commonly used by businesses, banks, and investors to manage their exposure to fluctuations in interest rates.
In this article, Forex Prop Reviews will explain interest rate swaps: how they work and their benefits.
What is an Interest Rate Swap?
An interest rate swap is a financial agreement where two parties exchange interest payments on a predetermined amount of principal, allowing them to manage their cash flow and reduce potential risks.
In other words, it's like a deal where one party agrees to pay a fixed interest rate while the other party pays a variable interest rate based on certain factors like inflation rates or market conditions.
This arrangement can be beneficial for both parties involved as it allows them to hedge against fluctuations in interest rates and create strategies that align with their financial goals.
Interest rate swaps work by providing flexibility in managing cash flow. For example, if one party expects interest rates to rise in the future, they may choose to pay a fixed rate so that they are protected from any increase.
On the other hand, if another party believes that interest rates will decrease, they may opt for paying a variable rate to take advantage of potential savings. By exchanging these payments, both parties can effectively manage their exposure to changing interest rates.

Types of Interest Rate Swaps
Here are three main types of interest rate swaps:
Fixed-to-Floating
Moreover, the fixed-to-floating interest rate swap allows parties to mitigate interest rate risk by exchanging a fixed interest payment for a floating one. In this type of swap, one party agrees to pay a fixed interest rate on a notional principal amount while receiving the floating rate from the other party. This arrangement provides flexibility and protection against fluctuating interest rates.
Here are some key features of the fixed-to-floating interest rate swap:
- Hedging tool: The fixed-to-floating swap is commonly used as a hedging tool to manage exposure to interest rate movements. By entering into this agreement, one party can protect themselves against potential increases or decreases in interest rates.
- Floating rate index: The floating leg of this swap is typically based on an agreed-upon benchmark such as LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate) or EURIBOR (Euro Interbank Offered Rate). This ensures that the payment reflects the prevailing market conditions.
- Duration of the swap: The duration of a fixed-to-floating swap can vary depending on the needs and objectives of both parties involved. It can range from several months to multiple years.
- Counterparty credit risk: As with any derivative contract, there is counterparty credit risk associated with fixed-to-floating swaps. Parties need to carefully assess and monitor each other's creditworthiness before entering into such agreements.
- Flexibility in cash flows: With a fixed-to-floating swap, parties have flexibility in managing their cash flows. For instance, if one party expects their future cash flows to be more variable due to changing market conditions, they may opt for receiving floating payments instead of paying a fixed amount.
Floating-to-Fixed
The floating-to-fixed interest rate swap allows you to exchange a fluctuating payment for a predetermined fixed payment. This provides you with stability and certainty in your cash flows, which is extremely beneficial for your financial planning.
With a floating-to-fixed swap, you can protect yourself from any potential increase in interest rates, as you’re locking in a fixed rate for the duration of the swap. This helps you avoid any unexpected increases in your payment obligations and allows you to budget more effectively.
Float-to-Float
One advantage of the float-to-float swap is that it allows you to diversify your interest rate exposure by exchanging one variable payment for another variable payment based on different reference rates. In this type of swap, both parties agree to exchange payments based on floating interest rates tied to different benchmarks.
For example, you could agree to pay a floating rate based on LIBOR while receiving a floating rate based on the Fed Funds Rate. This can be beneficial because it reduces your reliance on a single reference rate and spreads out your risk across multiple markets.
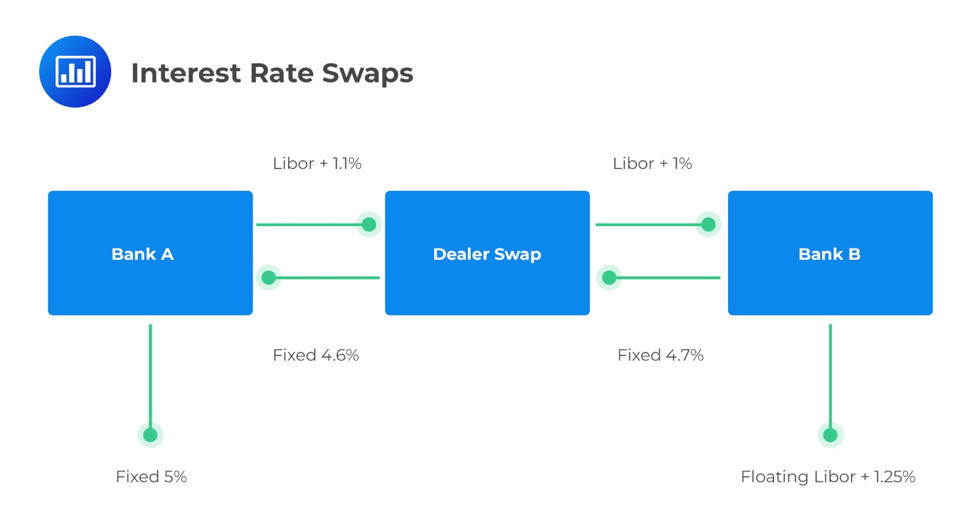
Real-World Example of an Interest Rate Swap
Imagine you're a financial analyst, and you've just come across a real-world example of an interest rate swap that'll leave you intrigued and wanting to learn more.
Let's say there are two companies, Company A and Company B. Company A has taken out a variable-rate loan with their bank, while Company B has opted for a fixed-rate loan. However, due to changes in market conditions, both companies find themselves facing unfavorable interest rates for their respective loans.
In this scenario, Company A approaches Company B with an interesting proposition: they suggest swapping their loans so that each company can benefit from the other's favorable interest rate terms. By entering into an interest rate swap agreement, both companies can effectively hedge against the risks associated with their original loans.
This real-world example showcases how interest rate swaps can be used as a strategic tool to manage risk and optimize financing options.

Benefits of Interest Rate Swaps
As a financial analyst, I discovered that interest rate swaps offer businesses the advantage of managing cash flows and minimizing exposure to fluctuating interest rates. They provide several benefits that can greatly impact a company's financial stability.
- Flexibility: Interest rate swaps allow businesses to customize their debt structure by converting fixed-rate loans into floating-rate loans or vice versa. This flexibility enables companies to align their borrowing costs with market conditions and adapt to changing economic environments.
- Risk management: By entering into an interest rate swap, businesses can effectively hedge against interest rate risks. For example, if a company has taken out a loan with a variable interest rate but wants protection against future increases in rates, it can enter into a swap agreement to convert it into a fixed-rate loan. This reduces the uncertainty associated with interest rate fluctuations and helps stabilize cash flows.
- Cost savings: Interest rate swaps can lead to significant cost savings for businesses. By accessing different markets and taking advantage of favorable interest rates, companies can achieve lower borrowing costs compared to traditional financing options. This not only improves profitability but also enhances competitiveness in the market.
You can learn more about the 5 strategies in interest and inflation rates strategies in this article.
How do they work?
Get ready to dive into the inner workings of these financial arrangements that can help you navigate through turbulent interest rate waters.
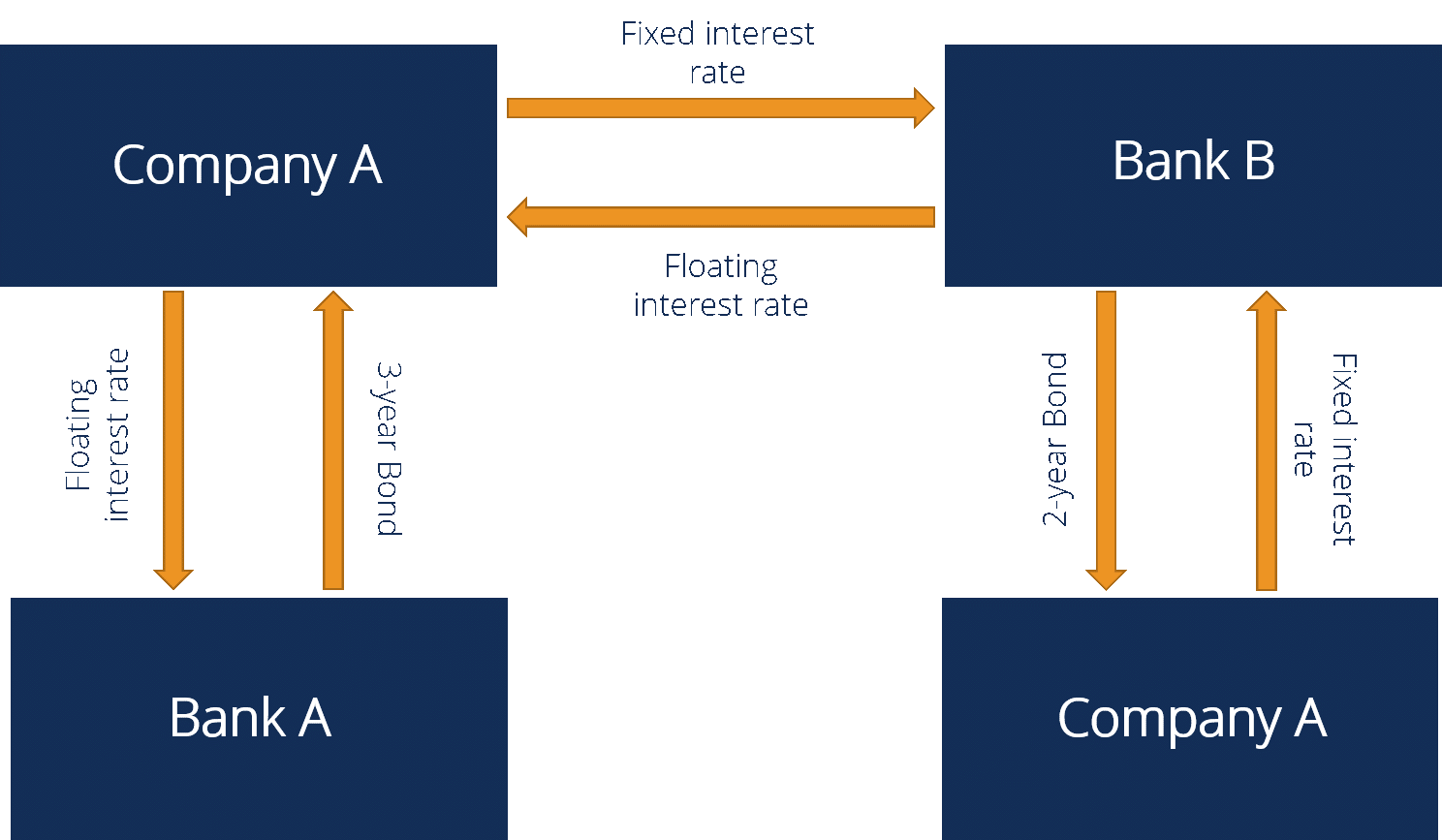
Interest rate swaps are contracts between two parties, typically a bank and a borrower, where they agree to exchange fixed and floating interest rate payments based on a notional amount.
The purpose of an interest rate swap is to hedge against interest rate risk or to achieve more favorable borrowing terms.
Here's how it works: you have a loan with a variable interest rate, which means your monthly payments fluctuate with market conditions. However, you prefer the stability of a fixed payment. So, you enter into an interest-rate swap agreement with your bank.
In this agreement, you agree to pay your bank a fixed interest rate on the notional amount while they agree to pay you the floating (variable) interest rate on the same notional amount.
By doing so, you effectively convert your variable-rate loan into a fixed-rate loan without actually refinancing it. This allows you to budget more accurately as your monthly payments remain constant regardless of any changes in market rates.
Additionally, if market rates were to increase significantly in the future, you would benefit from receiving the lower floating (variable) rate from the bank.
Interest rate swaps provide flexibility for both parties involved and can be tailored to their specific needs and objectives. They offer an effective tool for managing risk and creating favorable borrowing conditions in today's dynamic financial landscape.
Conclusion
Overall, understanding how interest rate swaps work and their potential advantages can empower individuals and companies to make informed financial decisions. Whether it's reducing risk exposure or optimizing cash flow management, these swaps offer a flexible solution for navigating the complex world of interest rates.




